The key to understanding the balance between the equity ratio and the debt ratio lies in how they interact with each other. As two key components of a company’s capital structure, their inverse correlation often provides meaningful insights into a company’s financial health. The lower the equity ratio, the more of a company’s assets are funded by debt and the riskier it is to invest in. In other words, all of the assets and equity reported on the balance sheet are included in the equity ratio calculation.
Get this exclusive AI content editing guide.
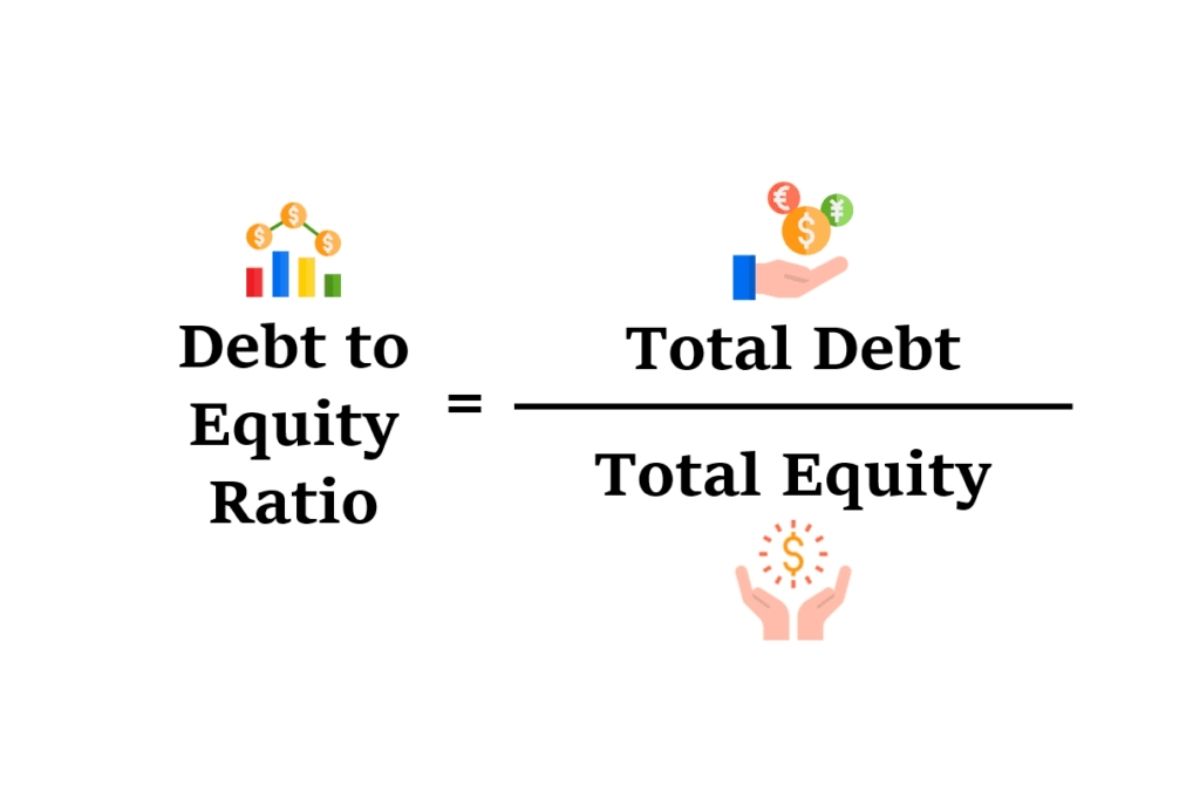
The lower the ratio result, the more debt a company has used to pay for its assets. It also shows how much shareholders might receive in the event that the company is forced into liquidation. The formula for calculating the equity ratio is equal to shareholders’ equity divided by the difference between total assets and intangible assets. The equity ratio is a financial metric that measures the amount of leverage used by a company. It uses investments in assets and the amount of equity to determine how well a company manages its debts and funds its asset requirements. The Debt to Equity ratio is a financial metric that compares a company’s total debt to its shareholder equity.
What are the Components of Shareholders Equity?

This includes anything that can be transformed into cash or that adds value to the company. Examples of assets might include real estate, machinery, vehicles, cash, investments, and inventory. As a value investor, you should never rely on a single ratio or investing metric to make your investment decisions. This lower ratio value can be relatively easy to sustain when a business is in an industry with inherently low levels of competition, and relatively stable sales and profits.
How does one calculate average equity?
Retaining ProfitsInstead of distributing all the profits as dividends among shareholders, a company can choose to retain a portion. As retained earnings are part of the owner’s equity, this strategy can help in increasing the equity ratio. Hence, it’s imperative to maintain a higher equity ratio, as it epitomizes financial stability, demonstrating to the lenders that the business is not excessively reliant on borrowed funds for its operations. It is a strategic financial indicator that has a profound impact on a company’s borrowing capabilities. Credit analysts employ the equity ratio because it provides a clear indication of the company’s long-term solvency. If the equity ratio is high, it demonstrates that a significant portion of the company’s assets is funded by its equity, meaning the company has less debt and therefore, lesser risk of default.
- While this can be a sign of potential financial instability, it might also just show that the company is aggressively leveraging debt to fuel growth.
- Retaining ProfitsInstead of distributing all the profits as dividends among shareholders, a company can choose to retain a portion.
- Other creditors, including suppliers, bondholders, and preferred shareholders, are repaid before common shareholders.
- By comparing total equity to total assets belonging to a company, the shareholders equity ratio is thus a measure of the proportion of a company’s asset base financed via equity.
Accounting Close Explained: A Comprehensive Guide to the Process
This means that if Company K were to sell all of its assets to pay off its liabilities, investors would retain ownership of ¾ of the company’s resources. The higher the ratio value, the more solvent a company is considered to be, since shareholder-owned assets are in excess of the firm’s liabilities. When you evaluate a business as a potential investment, it’s important to find out as much as possible about its debt situation and its financial sustainability over the long-term. The ROE ratio shows how a firm’s management has been able to utilize the resources at its disposal.
But an important distinction is that the decline in equity value occurs due to the “book value of equity”, rather than the market value. Enter your email to receive our weekly G2 Tea newsletter with the hottest marketing news, trends, and expert opinions. Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. By submitting this form, you consent to receive email from Wall Street Prep and agree to our terms of use and privacy policy. We’ll now move to a modeling exercise, which you can access by filling out the form below.
So, while the equity ratio alone provides key insights, it’s important to use it in combination with other financial indicators and context. It’s much like a piece in a financial jigsaw puzzle – immensely useful, but it doesn’t show the complete picture by itself. Just the same, investors usually prefer to see a higher ratio since it demonstrates a more conservative approach to debt management. As always, your interpretation of how high or low an acceptable shareholders’ capital ratio value is for a specific company will hinge on other available information.
Short-term profitability should not jeopardize the overall financial health of the company. Issuing SharesAnother common way for companies to increase equity editing and deleting invoices is by issuing additional shares. While this can lead to dilution of ownership, it is a viable way to raise additional capital without incurring debt.
